Hello Guys My Name is Aman From CBSEMeterials – Free CBSE Study Meterials and Today I am going to share Development Class 10 Notes For Free Which Helps you in Getting Good Marks in Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Notes. You can also download Development Class 10 Notes Pdf For Free of Cost. So without further ado, let’s get to the Economics Class 10 Chapter 1 Notes
TOPIC-1 ‘National Development’
Quick Review
- Progress is a synonym for development. We have always known its concept.
- Every person has personal goals and objectives for what he or she would want to achieve with their lives.
- Individuals desire consistent employment, higher pay, and a fair price for their produce or other goods. They want more incomes, in other terms.
- In addition to wanting more money, individuals desire respect for others, freedom, equality, and security. They also detest prejudice.
- Various types of people may have various growth objectives. A rural jobless person would desire greater employment chances in the village, job stability, and the dignity of labour, as opposed to an urban unemployed kid who would desire a goodsalaried job, promotions, etc.
- The most crucial element of progress is income.
- Their national income and per capita income are taken into consideration as a baseline point when comparing different nations.
- People have various aims, thus it stands to reason that they also have varied ideas about what constitutes national progress.
- Only per capita income is taken into account by the World Bank as a development indicator.
- The UNDP uses citizen per capita income, health, and educational attainment as indicators of development.
- According to the World Bank’s definition, affluent nations are those with a per capita income of US $ 12616 or more annually, whereas low-income countries have a per capita income of US $ 1035 or less.
- India falls under the category of low-income nations due to its meagre per capita income of US$1530 in 2004.
- The infant mortality rate (IMR), literacy rate, net attendance ratio, human development index, and accessibility to services are other factors to consider when comparing two states or nations.
- Income on its alone is not a reliable barometer of the people’s access to material goods and services. For instance, money cannot purchase a clean environment.
- Kerala has a high literacy rate and a low infant mortality rate (IMR) since there are many medical and educational resources available there.
Flowchart
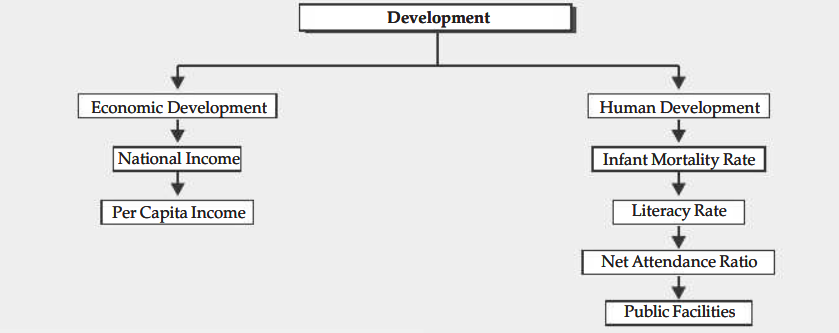
Important Terms
- Development : Growth translates into increased income, and to achieve that, people need consistent employment, better pay, and fair and acceptable prices for their goods.
- National Development : Increased per capita income and economic self-sufficiency are both indicators of national development.
- Sustainable Economic Development : The method of economic growth known as “sustainable development” strives to preserve current and future generations’ quality of life while without depleting the environment or natural resources.
- Economic Activities : Actions that generate income or, to put it simply, activities involving money.
- Non-economic Activities : activities that don’t involve money or that don’t generate income.
- Economic Development : Economic development is the process through which a nation’s gross domestic product and per capita income increase, and as a result, fewer people live in poverty, more employment opportunities are generated, and the standard of life for those in the lowest socioeconomic bracket of society increases.
- National Income : It is made up of the entire amount of finished products and services produced in a nation during a specific time period plus net factor income from overseas.
- Per Capita Income : Average annual income in a nation.
- Developing Countries : “Developing Countries” are nations where the level of living increases along with income.
- Underdeveloped Country : A nation is said to be “Underdeveloped” if its income is low and its level of living is similarly low.
- Economy : The economic framework that aids in describing the nation’s and its citizens’ economic lives.
TOPIC-2 ‘Public Facilities’
Quick Review
- Public facilities are those that the government makes available to the general public.
- The quality of life that inhabitants and others enjoy in urban environments is significantly impacted by the availability of public services and amenities.
- In order to build strong, resilient, healthy, and cohesive communities, remove social barriers, and improve performance, public amenities are crucial.
- All the products and services that one could require to live properly cannot be purchased with money alone.
- The ability of persons to consume material goods and services cannot always be determined solely by income.
- Some necessary services, including as healthcare, sanitation, energy, public transportation, and educational institutions, must be provided by the government.
- Kerala has a low infant mortality rate since there are many basic medical and educational resources available there.
- The Public Distribution System (PDS) runs well in several states. In these locations, if a PDS shop, or ration shop, is not operating effectively, the locals can get the issue fixed. Those living in such states are almost probably more likely to have better health and nutritional condition.
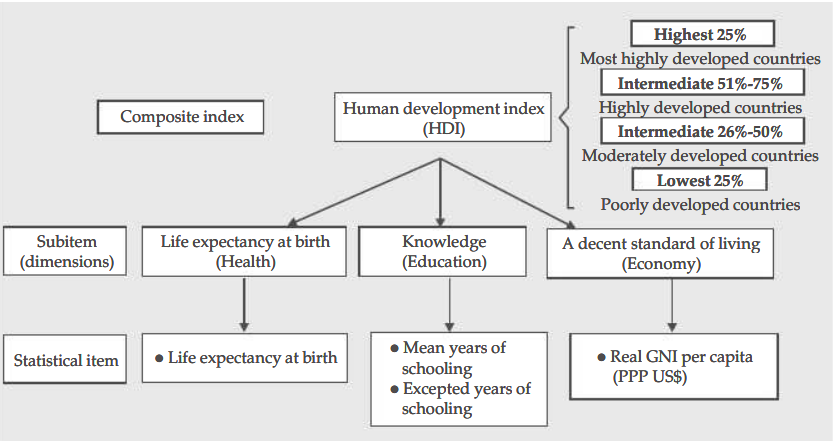
- In its Human Development Report, the UNDP evaluates nations based on the people’s per capita income, health status, and educational attainment levels.
- Countries are ranked into four categories of human development using the Human Development Index (HDI), a composite statistic combining life expectancy, education, and per capita income factors.
- India is ranked 126 worldwide by the HDI.
- The developmental objective includes freedom, education, security, and peace in addition to having a higher income and receiving fair treatment.
- These aspirations of diverse facets of society for their own growth can be fulfilled through democratic political processes.
- The UNDP’s Human Development Index shows a country’s degree of progress, how far it has gone, and how far it still has to go to score well in areas like per capita income, welfare components including life expectancy, literacy, educational attainment, and health status, among others.
More SST Notes
Flowchart
Important Terms
- Infant Mortality Rate : the proportion of infant deaths under one year old per 1,000 live births in a given year.
- Literacy Rate : population literacy rate for those aged 7 and older.
- Net Attendance Ratio : As a proportion of all children in the same age range, the total number of 6 to 10 year olds enrolled in school.
- Human Development Index : The human development index, which ranks nations into four levels of human development, is a composite statistic comprising life expectancy, education, and per capita income data.
TOPIC-3
Sustainability of Development
Quick Review
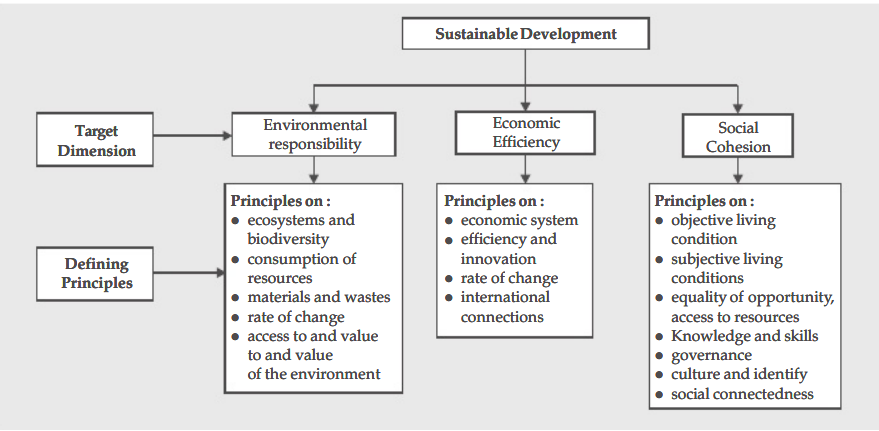
- Economic growth that is sustainable means that it shouldn’t harm the environment and that it shouldn’t put current demands ahead of those of the next generation.
- The various measures for sustainable development are :
- Controlling over uses and creating an awareness to provide sustainable development.
- Increased use of renewable resources.
- Less use of fossil fuels.
- Introduction of organic farming.
- Adopting measures to reduce global warming.
- Sustainable development is all about using resources wisely today while considering the needs of future generations, such as groundwater.
- As water is a renewable resource, we must contribute to its replenishment because groundwater is overused for agriculture.
- Sustainable development is important for economic growth because :
- As development is occurring, the environment must be preserved.
- It is necessary to use resources in a way that preserves something for future generations.
- Every people’s living conditions must be improved.
- The globe contains enough resources to meet everyone’s needs, but not enough to sate even one person’s greed, according to Mahatma Gandhi.
- Environmental deterioration has effects that cross state and national boundaries.
- Working together, scientists, economists, philosophers, and other social scientists are developing a body of knowledge about sustainable development.
Flowchart
Important Terms
- Sustainable Development : Maintaining sustainable development involves striking a careful balance between the desire for people to better their lifestyles and sense of wellbeing on the one hand, and protecting the ecosystems and natural resources that are essential to us and future generations on the other.
- Organic Farming : Production of vegetables and cattle utilising organic techniques of crop and weed management rather than synthetic or inorganic agrochemicals, and natural sources of nutrients (such as compost, crop leftovers, and manure).
- Fossil Fuels : a natural fuel that was formerly generated from the remnants of living things, such as coal or gas.
- Global Farming : a slow rise in atmospheric temperature that is typically linked to the greenhouse effect, which is brought on by higher quantities of pollutants like carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons.



