Hello Guys My Name is Aman From CBSEMeterials – Free CBSE Study Meterials and Today I am going to share Federalism Class 10 Notes For Free Which Helps you in Getting Good Marks in Class 10 Civics Chapter 7 Notes. You can also download Outcomes Of Democracy Class 10 Notes Pdf For Free of Cost. So without further ado, let’s get to the Civics Class 10 Chapter 7 Notes
TOPIC-1 ‘How Do We Assess Democracy’s Outcomes ?’
Quick Review
Is Democracy a better form of government when compared with
dictatorship or any other alternative ?
The benefits of democracy include :
(i) It encourages societal equality.
(ii) It raises a person’s sense of dignity.
(iii) It raises the standard of judgement in decision-making.
(iv) It offers a technique for resolving disputes.
(v) It gives room for error correction.
Is the democratic government efficient? Is it effective ?
⦿ Consider a different type of government that might make decisions quickly. However, it might make judgements that the public does not agree with, which could lead to issues.
⦿ Deliberation and negotiation are the cornerstones of democracy. Therefore, a delay will undoubtedly occur.
⦿ The democratic government, on the other hand, will take more time to follow procedures before making a decision.
⦿ But because it adhered to protocol, its choices might be more popular with the populace and more useful.
⦿ Therefore, the time investment that democracy makes may be worthwhile.
Outcomes out of every democracy :
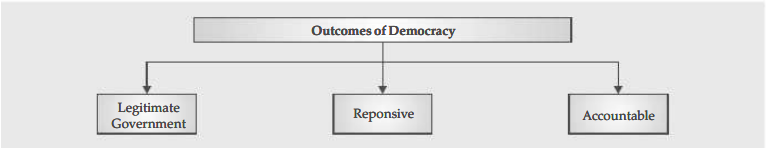
⦿ We anticipate a legitimate, responsive, and responsible government as a political result of democracy.
⦿ We anticipate that democracies will result in economic growth and development, as well as a decrease in poverty and inequality.
⦿ As a social outcome, we anticipate that democracy will allow for social diversity in a society and guarantee everyone’s freedom and dignity.
Flowchart

Important Terms
- Dictatorship : All of the power is concentrated in the hands of a single person or group of persons under a dictatorship.
- Legitimate government : Legitimate government is that which has been legally chosen.
- Transparency : to investigate how a democracy makes decisions.
TOPIC-2 ‘Outcomes Of Democracy‘
Quick Review
Democracy is a form of legitimate, responsive, and accountable government.
- Democracy makes ensuring that decisions are made in accordance with rules and regulations. Therefore, a citizen has the authority and tools to investigate how decisions are made. Transparency is what is meant here. Democracy is responsible to the people and operates according to rules.
- When it comes to sharing information with the public, democratic governments have a very solid track record and fare significantly better than any non-democratic system. Democracy pays attention to the wants and requirements of the populace and is largely corruption-free.
- Democratic governance is unquestionably superior to its alternatives in one area: it is a valid form of government. It might not always be quick, effective, responsive, or clean. A democratic government, however, is one that the people control.
Flowchart
Important Terms
- Accountable government : the representative government, which is accountable to the people.
- Responsive government : the type of government where citizens have a right to information about how decisions are made.
TOPIC-3 ‘Economic Outcomes’
Quick Review
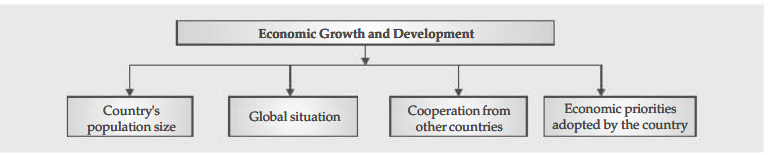
Economic development and growth
- Numerous variables affect economic development, including the size of the nation’s population, the state of the world, international cooperation, the priorities the nation has set for its economy, etc.
- The rates of economic progress of less developed nations with dictatorships and democracies, however, barely differ from one another.
- In general, we cannot assert that democracy is a sine qua non of economic growth. But we may anticipate that democracies won’t trail behind autocracies in terms of economic advancement.
Democracy lowers poverty and economic inequality
- Economic inequality is rising in democracies. Those at the bottom of society have very little to rely on and find it very difficult to meet their fundamental needs of life, such as food, clothing, a place to live, education, and health. A small number of extremely wealthy people enjoy the lion’s share of money.
- Democratically elected governments tackle the issue of poverty by implementing a variety of welfare programmes to end it.
- In addition to creating welfare programmes, democracies grant socially and economically disadvantaged individuals preferences in employment, elections, and educational institutions.
Flowchart
Important Terms
- Economic Development : It is the growth of the economic prosperity of nations, regions, or communities for the benefit of the local populace.
- Dictatorship : a system of government where the tyrant has total authority.
- Economic Inequality : It is the variance in many metrics of economic well-being across people, between groups within a population, or between nations.
TOPIC-4 ‘Social Outcomes’
Quick Review
Democracies allow for social diversity
- Typically, democracies create a process to accommodate multiple social groupings. This lessens the likelihood that social tensions may blow up or turn violent.
- Conflicts between various groups cannot be completely and permanently resolved by any society. However, democracy works best to resolve societal problems, divisions, and disagreements.
- But the experience of Sri Lanka serves as a reminder that in order to accommodate socioeconomic divisions, a democracy must meet two requirements:
- It is important to realise that democracy is more complicated than just majority rule. To ensure that governments function to represent the dominant viewpoint, the majority must always cooperate with the minority.
- Furthermore, it is essential to prevent majority rule from becoming into majority community in terms of race, religion, linguistic group, etc. Rule by majority refers to a group’s decision.
Democracy encourages citizens’ freedom and dignity.
- By establishing Fundamental Rights, democracy outperforms all other forms of governance in fostering individual freedom and dignity. Everyone desires to be respected by other people.
- Democracy is built on a hunger for respect and freedom. This is acknowledged by democracies everywhere, at least in theory. In many democracies, this has been accomplished to varying degrees.
- Consider the issue of women’s dignity. The majority of societies in the globe have historically been governed by men.
- Today, some people are sensitive to the fact that respect for and equitable treatment of women are essential components of a democratic society due to the long battles of women.
- The castes that are underrepresented and subject to discrimination now have stronger arguments for equal opportunity and status.
Flowchart
Important Points
- Social Diversity : It is any distinction made between individuals within a particular culture. Social variety can be characterised by factors including race, way of life, religion, language, tastes, and preferences.
- Social divisions : Social division occurs when there are growing social divides between several communities and when one community experiences discrimination as a result. For instance, social divide between top and lower castes occurs because dalits are typically poor and experience injustice and prejudice.
Conclusion
⦿ A democracy constantly strives to achieve greater success. In a democracy, there is a perpetual demand for additional advantages. More expectations are constantly present.
⦿ People today evaluate the work of people in positions of authority, the wealthy, and the powerful critically. They vocally voice their displeasure. It demonstrates that they are no longer subjects but rather citizens of a democracy.



