Hello Guys My Name is Ayan From CBSEMeterials – Free CBSE Study Meterials and Today I am going to share Federalism Class 10 Notes For Free Which Helps you in Getting Good Marks in Class 10 Civics Chapter 2 Notes. You can also download Democracy and Diversity Class 10 Notes Pdf For Free of Cost. So without further ado, let’s get to the Civics Class 10 Chapter 2 Notes
Contents
hide
TOPIC-1
Gender and Politics
Quick Review
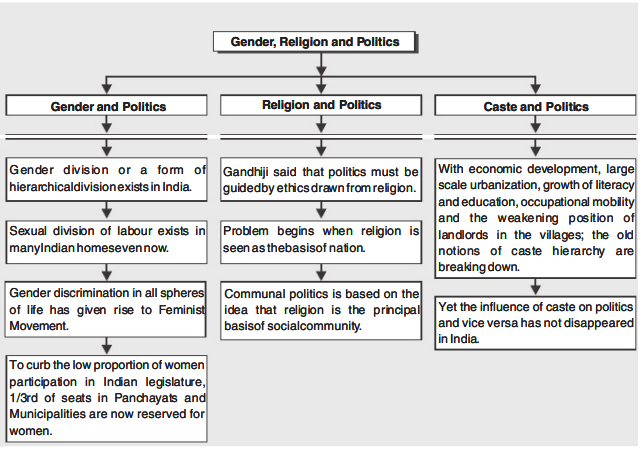
- Gender inequality is a prevalent example of hierarchical social division.
- The term “sexual division of labor” refers to the division of labor among individuals based on sex.
- Casteism, gender inequity, and sectarian divisions all serve as strong indicators of how Indian society is divided on a social level.
- In the past, men could only vote, participate in politics, and run for public office. Politics gradually began to address the gender issue.
- Women organized and fought for equal rights throughout the world.
- These protests called for increasing women’s political and legal standing as well as their educational and employment possibilities.
- Feminists can be either men or women who support equal rights and opportunity for both sexes.
- The majority of women’s movements strive for gender equality in both women’s personal and familial lives. Feminist movements are what these movements are known as.
- India still has a patriarchal society that is ruled by men.
- Women experience disadvantage, prejudice, and oppression in a variety of ways, including being less literate, working as hard but occasionally earning less than males, having their sons raised by their parents more often, etc.
- The percentage of women in the legislature in India has historically been quite low.
- A equitable representation of women in the elected bodies has been mandated by law in India’s Panchayati Raj in order to address this issue.
- Women now hold one-third of the seats in local government organizations, including Panchayats and Municipalities.
- One societal division that needs to be expressed in politics is the one based on gender.
Flowchart
Important Terms of Gender Religion and Caste Class 10 Notes
- Gender Division : It is a type of social separation based on hierarchy and stereotypes in society.
- Sex Ratio : It is the ratio of females to males in a nation throughout a specific time period.
- Communal Politics : Community politics refers to the political use of religion in which one religion is portrayed as being superior to all others.
- Sexual Division of Labour : a system in which the ladies of the household either carry out all domestic work themselves or organize it through domestic servants.
- Feminist : a person who favors granting all people the same opportunity and rights.
- Patriarchy : a system in which the father serves as the family’s head.
- Stereotype : a commonly held perception or idea of a specific kind of person or thing that has become fixed.
- Feminism : It is concerned with empowering women and ensuring that they have an equal place in society to males.
TOPIC-2
Religion, Communalism and Politics
Quick Review
- The caste system, communalism, illiteracy, unemployment, and poverty are challenges for the Indian democracy.
- Minorities are social groups in a society with a comparatively small population.
- Communal representation is a system that creates separate electorates and representation for members of various communities.
- Family laws are those that govern issues pertaining to families, such as marriage, divorce, and other related issues.
- The two main religions in Sri Lanka and Nepal are Buddhism and Hinduism, respectively.
- Political exploitation of religion is referred to as communal politics.
- Politics may and perhaps should incorporate beliefs, ideas, and values from several religions.
- As members of a religious community, people should be able to express their needs, interests, and demands in politics.
- The fundamental tenet of communal politics is that religion serves as the cornerstone of social community.
- In politics, communalism can take many different shapes :
- Commonplace beliefs are where communalism is most frequently seen.
- The desire for political domination within one’s own religious community is frequently the result of a communal mindset.
- Another common manifestation of communalism is political mobilization along religious lines.
- Community violence, riots, and massacres are occasionally the most obscene manifestations of communalism.
- There is no recognized state religion in a secular nation like India.
- The Constitution guarantees every person and community the freedom to profess, practice, and spread any religion—or no religion at all. Among its attributes are:
- Religion-based discrimination is forbidden by the Constitution.
- In order to guarantee equality within religious communities, the Constitution also permits the state to get involved in religious concerns.
Flowchart

Important Terms of Gender Religion and Caste Class 10 Notes
- Communalism : It refers to initiatives to spread religious doctrine among social groupings that have been designated by various societies.
- Family Laws : In our nation, distinct family laws apply to adherents of different religions when it comes to family-related issues like marriage, divorce, adoption, inheritance, etc.
- Literacy Rate : The literacy rate measures the proportion of educated citizens to the total population of a nation.
- Prejudice : an irrational hate or preference, especially one that is based on the race, religion, sex, or other characteristics of a person, group, or habit.
- Secular State : a country where there is no recognized religion. It accords all religions an equal standing.
- Secularism : a conviction that religion shouldn’t play a role in how society is run.
- Urbanisation : population shift from rural to urban areas.
TOPIC-3
Caste and Politics
Quick Review
- Casteism is a behavior that makes members of higher castes detest those of lower castes.
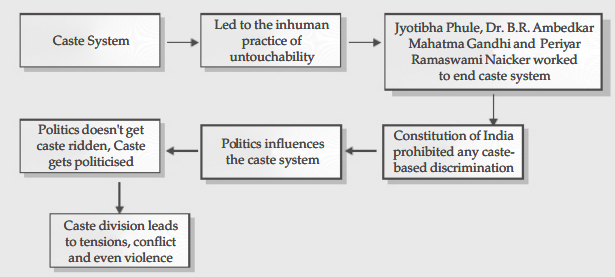
- The foundation of the caste system was the prejudice and exclusion of the “outcaste” communities. They were made to suffer under the cruel custom of untouchability.
- Gandhiji opposed becoming an untouchable.
- The caste system in India was fought against by Jyotiba Phule, Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, Mahatma Gandhi, and Periyar Ramaswami Naicker.
- The traditional ideas of caste hierarchy are disintegrating due to economic expansion, widespread urbanization, increases in literacy and education, job mobility, and the weakened status of landlords in rural areas.
- The Indian Constitution forbade any kind of caste-based discrimination and established the framework for measures to undo the injustices of the caste system.
- No parliamentary district in the nation is clearly dominated by a particular caste.
- By integrating caste into the political sphere, politics also has an impact on caste identities and the caste system.
- A number of political and non-political organizations have been clamoring for the elimination of caste-based discrimination, greater dignity, and increased access to land, resources, and opportunities.
- Caste can draw attention away from more urgent problems including poverty, development, and corruption.
- Caste division can occasionally cause tensions, disputes, and even violence.
Flowchart
Important Terms Class 10 Civics Chapter 4 Notes
- Urbanisation : population shift from rural to urban areas.
- Casteism : The hereditary structure of social class, culture, endogamy, and occupation is known as casteism. It is often referred to as a class system that is based on birth.
- Dalits : The Dalits, who belong to the Scheduled Castes (SCs), are well-known.
- Adivasis : The STs are also referred to as Adivasis.
- Caste Hierarchy : All caste groupings are arranged in a ladder-like structure, from the highest to the lowest.
- Electorate : everyone who is qualified to cast a ballot in an election inside a nation or region.
- Universal Adult Franchise : It indicates that everyone who is a citizen and is at least 18 years old has the right to vote.
- Occupational Mobility : a change in occupation, typically when a new generation chooses a profession that was not performed by their predecessors.



