Hello Guys My Name is Aman From CBSEMeterials – Free CBSE Study Meterials and Today I am going to share Money And Credit Class 10 Notes For Free Which Helps you in Getting Good Marks in Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Notes. You can also download Money And Credit Class 10 Notes Pdf For Free of Cost. So without further ado, let’s get to the Economics Class 10 Chapter 3 Notes
TOPIC-1
Money and Credit
Quick Review
- According to their needs, individuals would swap one good for another in the early days using the barter system. Yet, the barter system needed two wants to coincide in order to exchange things.
- Money, however, does away with the requirement for two desires to coincide. Money is sometimes referred to as a medium of exchange since it facilitates the trade process. Early money was made of everyday items.
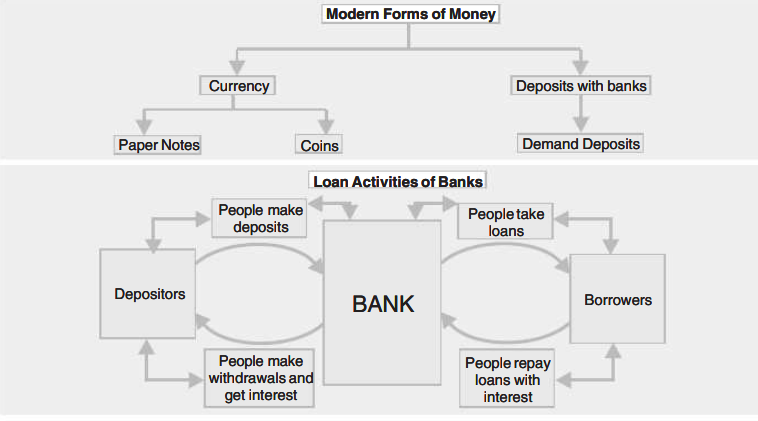
- Modern currency :
- use coins and paper currency manufactured of very affordable metals.
- is worthless on its own.
- only has value because it has been approved by the national government.
- Only the Reserve Bank of India is authorised by law to print money on behalf of the national government in India. Everyone in India must accept payments made in rupees because it is the country’s official currency.
- They put their excess money in the bank. In addition to holding the money, a bank also pays the depositor interest on the deposit. As a result, demand deposits are another name for bank deposits.
- To deposit money, all one needs is an account with the bank. Without using cash, a cheque can be used to receive money immediately from a bank deposit.
- A check is a written directive from an account holder to a bank to use his deposit to pay a certain amount to a specific individual. A check includes all the necessary details on the recipient of the payment, the amount and date of the transaction, and the signature of the account holder issuing the check.
Flowcharts
Important Terms
- Barter System : The direct exchange of products and services is referred to as bartering. In this context, the term “barter system” refers to a method of exchanging one good for another without the need of cash.
- Money : Everything that the public chooses as a means of trade might be considered money. It can take the shape of coins and bank notes, either separately or all at once.
- Cheque : A check is a document that gives banks written instructions to withdraw a certain amount from a person’s account and pay it to the person listed on the check.
- Reserve Bank of India : Only the Reserve Bank of India is authorised by law to print banknotes and coins on behalf of the national government.
- Investment : Investments are sums of money spent with the goal of generating income over the long term or on a regular basis (in the form of returns from funds invested) (in the form of capital appreciation).
TOPIC-2
Credit Terms and Types
Quick Review
- According to the Reserve Bank of India, banks maintain 15% of their deposits in cash to facilitate depositors’ daily withdrawals.
- Banks use a sizable amount of the remaining deposits to make loans to individuals. A bank’s depositors have the right to withdrawal their funds upon request and receive interest on those funds. The money borrowed is paid back to the lender together with interest by the borrowers.
- In comparison to interest paid by banks on deposits, loan interest is higher. The bank’s income or profit is determined by the difference between the interest rates on loans and deposits.
- The term “credit” is also used to describe a bank loan.
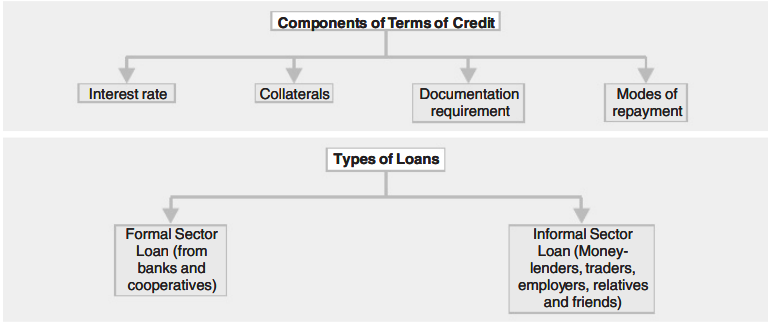
- A borrower must consent to a set of conditions before receiving a loan or credit. The terms of credit refer to these requirements, which include:
- a specific interest rate.
- If the borrower doesn’t pay back the loan, there is security against it to get the money back. We refer to this security as collateral.
- Land or other real estate, automobiles, cattle, standing crops, and bank savings are all acceptable forms of collateral.
- To be eligible for a loan, a borrower must provide documentation of their identification, place of residence, employment, and income.
- In the event of non-repayment, the lender maintains the right to sell the collateral in order to recoup the loan balance.
- Formal and Informal Credit
- The different sources of credit are :
- Banks
- Traders
- Cooperative societies
- Landlords
- Moneylenders
- Relatives and friends
- The different sources of credit are :
Flowcharts
Important Terms
- Credit : Giving money on credit to people in need.
- Financial Formal Institutions : The official institutions of credit include commercial banks, cooperatives, and local rural banks.
- Financial Informal Institutions : The local moneylenders, landlords, self-help groups, chit funds, employers, relatives, friends, and private finance corporations make up India’s informal system for allocating credit and savings.
- Commercial Bank : A commercial bank is a facility for the safekeeping of money that it disburses on a customer’s demand order or in some other way. Alternatively said, organisations that accept deposits and provide loans are referred to as commercial banks.
- Loans : A loan is often granted for a set period of time and must be fully returned by a certain date.
- Collateral : Collateral is the security offered by a borrower (such as real estate, a building, a car, livestock, or bank savings) against a loan and may be auctioned if the loan is not repaid.
- APS : Average Propensity to Saving is referred to as APS.
- Fiat Money : Money that is issued by the government that is neither set in value according to any objective standard nor legally convertible into anything else.
- Fiduciary Money : Fiduciary money is referred to as money that is accepted on the basis of the trust that the issuer commands.
- Fixed Deposits : These are fixed-term deposits with terms ranging from a few days to a few years.
- Actual Investment : An actual investment is one that is made in the full amount.
- Deferred Payments : Deferred payments are ones that need to be made in the future.
- Token coins : Token coins are those whose worth as currency is significantly more than the value of the metal they contain.
- Short-term loans : Short-term loans are loans that are provided for a little duration.



