Hello Guys My Name is Ayan From CBSEMeterials – Free CBSE Study Meterials and Today I am going to share Federalism Class 10 Notes For Free Which Helps you in Getting Good Marks in Class 10 Civics Chapter 2 Notes. You can also download Federalism Class 10 Notes Pdf For Free of Cost. So without further ado, let’s get to the Civics Class 10 Chapter 2 Notes
TOPIC-1
What is Federalism & What Makes India a Federal Country ?
Quick Review
- Federalism is the division of authority among the federal government, state, municipal, and regional administrations.
- There is a clear-cut division of powers between the Central authority and numerous Constituent units of the country in the federal form of government.
- Federal governments exist in Argentina, Austria, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Germany, India, Mexico, Switzerland, and the United States.
- Some states in the Indian Union are too small to become independent states and can’t be combined with other states that already exist. Union Territories are the name for these divisions.
The key features of federalism are :
- The number of levels (or tiers) of government is two or more.
- Although various levels of government administer the same individuals, each level has its own jurisdiction over certain issues related to law, taxation, and administration.
- The constitution specifies the jurisdictions of the various levels or tiers of government.
- No level of government may unilaterally alter the fundamental rules of the constitution.
- Both levels of government must agree on such reforms.
- Courts have the authority to interpret the Constitution and the authority of various governmental levels.
- Each level of government has clearly defined revenue sources to guarantee its financial independence.
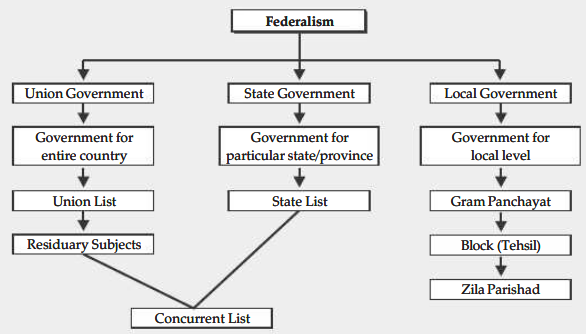
(i) The Union List include topics of national importance such the nation’s defense, international relations, banking, communications, and currency. The items listed in the Union List are only subject to legislative action by the Union Government.
(ii) The State List includes topics with national, regional, and local significance, including agriculture, irrigation, trade, and the police. Only the State Governments have the authority to enact legislation pertaining to the topics included in the State List.
(iii) Concurrent List contains topics including education, forests, trade unions, marriage, adoption, and succession that are of concern to both the Union Government and the State Governments. The governments of the Union and the States have the authority to pass laws on the issues listed here. If two states’ laws contradict, the Union Government’s law will take precedence.
Other Class 10 Notes
Flowchart
Important Terms in Federalism Class 10 Notes
- Federalism : Federalism is a form of government in which a central authority and numerous national constituent parts share power.
- Jurisdiction : the territory that they have the right to control.
- Union List : It covers important national issues. Only the Central Government has the authority to decide on issues like national defense, international relations, finances, and communications.
- State List : It covers important state-level issues. On certain issues, only the State Government has the authority to decide. They cover topics like law enforcement, commerce, trade, agriculture, and irrigation.
- Concurrent List : It covers topics including education, forestry, marriage, adoption, and succession as well as trade unions that are of importance to both the federal government and state governments. Governments at the Central and State levels decide these
- ‘Coming together’ Federation : It is a federation in which numerous independent states join forces on their own to create a larger organization so that they can strengthen their security by sharing sovereignty and maintaining their individual identities. The USA, Switzerland, and Australia are included.
- ‘Holding together’ Federation : It is a federation in which a sizable nation chooses to distribute its authority between the member states and the federal government. India, Spin, and Belgium are all part of it.
- Residuary Subjects : Topics that don’t fit into one of these three categories. Remaining subjects include new topics like computer software that emerged after the constitution was created.
- Unitary System : It is a form of governance where the subunits either report directly to the central government or there is only one level of government.
- Language Policy : It is the safeguard to other languages.In accordance with this principle, the Constitution also recognizes 21 additional languages in addition to Hindi as Scheduled Languages.
- Scheduled Languages : The Scheduled languages are the 22 languages that are listed in the Constitution’s Eighth Schedule.
- Indian Federation : There are 7 union territories and 29 states. New Delhi serves as its capital.
- Union Territories : These areas are directly governed by the federal or union government and lack state-like authority. Chandigarh, Lakshadweep, etc. are a few examples.
- Regionalism : a strong sense of devotion or pride for a specific area coupled with a desire for more autonomy.
TOPIC-2
How is Federalism Practiced Decentralisation in India ?
Quick Review
- The founding of Linguistic States was our nation’s first big democratic political test.
- The designated official tongue is Hindi. But in addition to Hindi, the Constitution also lists 22 other languages as Scheduled Languages.
- States like Nagaland, Uttarakhand, and Jharkhand were established to recognize differences based on culture, ethnicity, or geography rather than on the basis of language.
- Another way that federalism has been enhanced in practice is through restructuring the relationship between the Center and the States.
- When no one party wins a clear majority in the Lok Sabha, the major national parties establish an alliance with numerous other parties, including a number of regional parties, to form what is known as a coalition government at the center.
- In 1992, a significant step toward decentralization was made.
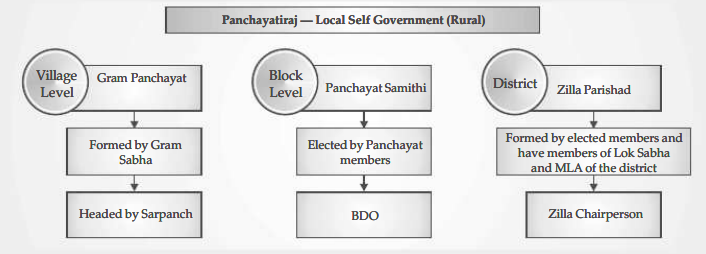
- Local government in rural areas is commonly referred to as Panchayati raj. There is a gram panchayat in every village or cluster of villages in various States.
- A panchayat samiti, block, or mandal is what is commonly referred to as a collection of gram panchayats.
- The Zilla (district) parishad is made up of each mandal or panchayat in a district.
- The political leader of the zilla parishad is the zilla parishad chairperson. Towns are where municipalities are built up. Municipal corporations are formed in large cities.
- Municipal corporations and municipalities are both governed by elected bodies made up of citizens’ representatives.
- The municipality’s political leader is the chairperson. A municipal corporation’s equivalent of this officer is the mayor.
To strengthen and improve the third tier of democracy, the Constitution was altered. The following actions were made in response to this:
The holding of regular elections for local governmental entities is required by the constitution.
The elected bodies and executive heads of these institutions have seats set aside for members of the Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes.
At least one-third of all jobs are held exclusively by women.
In order to conduct panchayat and municipal elections, each State has established an autonomous organization called the State Election Commission.
Local governmental entities must receive a portion of the authority and funding that state governments receive.
Flowchart
- Autonomy : a region or territory that is capable of independent government.
- Linguistic States: India is a multilingual nation where many languages are spoken. Following independence, certain states were established based on the languages that the populace spoke. The term “linguistic states” refers to them.
- State Election Commission : Each state has a body set up to handle municipal and panchayat elections.
- Panchayati Raj : a form of government where the fundamental administrative units are called Gram Panchayats. Gram (village), Tehsil (block), and Zila are its three tiers (District).
- Panchayat Samiti : It is an Indian local government body that sits between the Gram Panchayat and the Zila Parishad at the tehsil or taluka level.
- Gram Sabha : the organizations in charge of regulating Gram Panchayats.
- Tier System : The system denotes the many tiers of governance. It could have two levels (two tiers), three levels, or more (three tiers).
- Mayor : The term “mayor” refers to the head of a municipal corporation.
Conclusion
Thank You for Reading Federalism Class 10 Notes. I Hope the Civics Class 10 Chapter 2 Notes Created by CBSEMeterials.com Team May Found Helpful for Your Class 10 Exam Preparation. If Found Any Error or Suggestion Please to Let Us Know